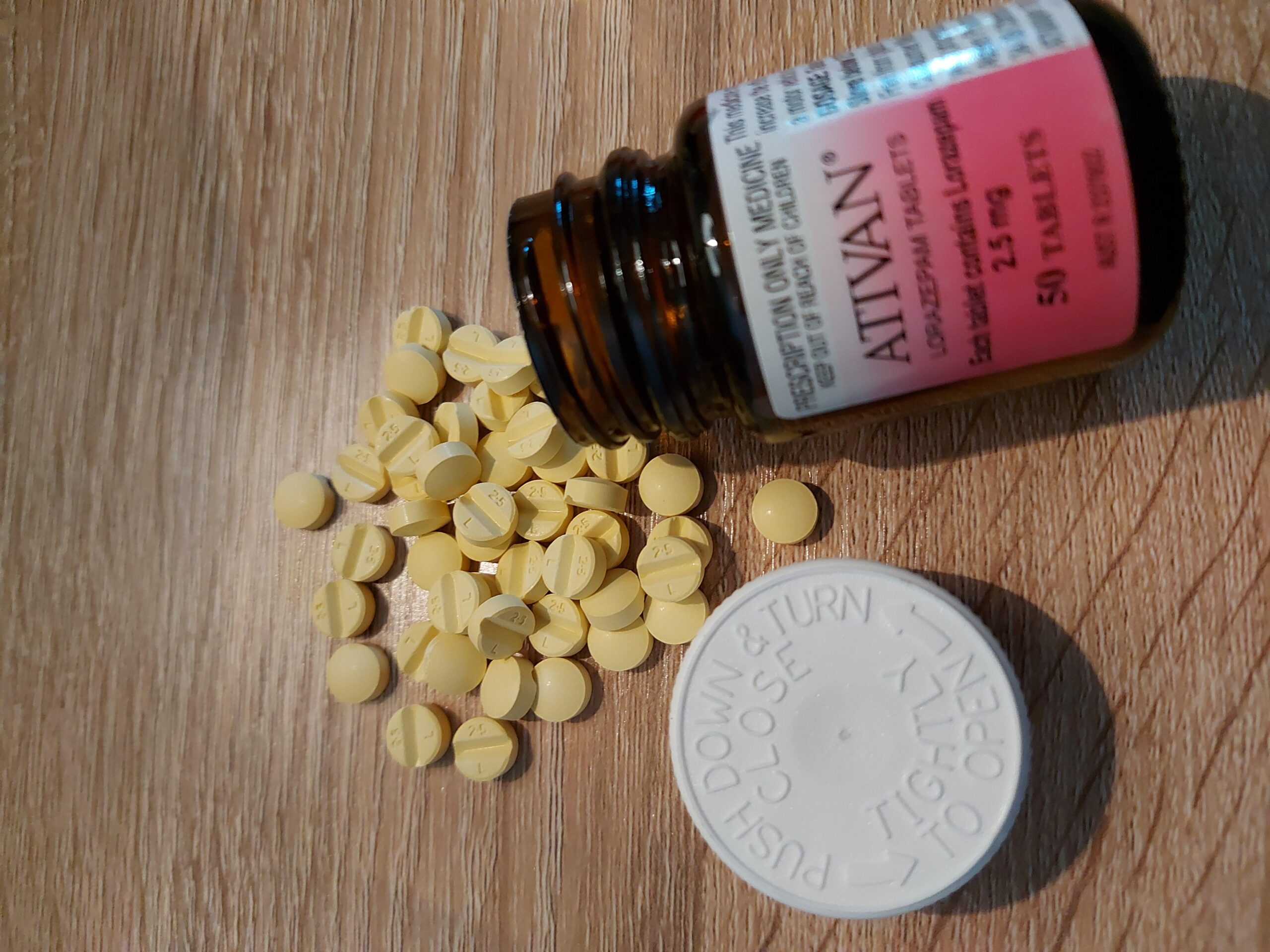
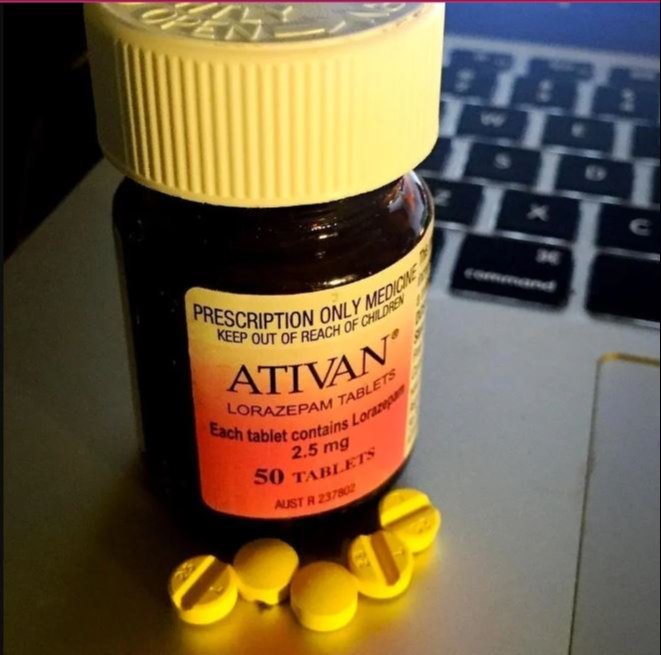
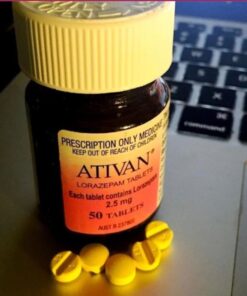
Ativan Lorazepam 2.5mg
$450 – $720
Buy Lorazepam (Ativan) 2.5 mg tablets online.
Buy Lorazepam (Ativan) 2.5 mg tablets online.Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication.[3] It is used to treat anxiety disorders, trouble sleeping, severe agitation, active seizures including status epilepticus, alcohol withdrawal, and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.[3] It is also used during surgery to interfere with memory formation and to sedate those who are being mechanically ventilated.[3][7] It is also used, along with other treatments, for acute coronary syndrome due to cocaine use.[3] It can be given by mouth or as an injection into a muscle or vein.[3] When given by injection, onset of effects is between one and thirty minutes and effects last for up to a day.[3]
Common side effects include weakness, sleepiness, low blood pressure, and a decreased effort to breathe.[3] When given intravenously, the person should be closely monitored.[3] Among those who are depressed, there may be an increased risk of suicide.[3][8] With long-term use, larger doses may be required for the same effect.[3] Physical dependence and psychological dependence may also occur.[3] If stopped suddenly after long-term use, benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome may occur.[3] Older people more often develop adverse effects.[9] In this age group, lorazepam is associated with falls and hip fractures.[10] Due to these concerns, lorazepam use is generally only recommended for up to two to four weeks.[11]
Lorazepam was initially patented in 1963 and went on sale in the United States in 1977.[12][13] It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.[14] It is available as a generic medication.[3] In 2020, it was the 65th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 10 million prescriptions.
Medical uses
Anxiety
Lorazepam is used in the short-term management of severe anxiety. In the US, the FDA advises against use of benzodiazepines such as lorazepam for longer than four weeks.[11][17] It is fast acting, and useful in treating fast onset panic anxiety.[18]
Lorazepam can effectively reduce agitation and induce sleep, and the duration of effects from a single dose makes it an appropriate choice for the short-term treatment of insomnia, especially in the presence of severe anxiety or night terrors. It has a fairly short duration of action.[19]
Withdrawal symptoms, including rebound insomnia and rebound anxiety, may occur after seven days’ use of lorazepam.[20]
Seizures

Intravenous diazepam or lorazepam are first-line treatments for convulsive status epilepticus.[21] Lorazepam is more effective than diazepam and intravenous phenytoin in the treatment of status epilepticus and has a lower risk of continuing seizures that might require additional medication.[22] However, phenobarbital has a superior success rate compared to lorazepam and other drugs, at least in the elderly.[23][24]
Lorazepam’s anticonvulsant properties and pharmacokinetic profile make intravenous use reliable for terminating acute seizures, but induce prolonged sedation. Oral benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, are occasionally used as long-term prophylactic treatment of resistant absence seizures; because of gradual tolerance to their anti-seizure effects, benzodiazepines such as lorazepam are not considered first-line therapies. Additionally, common seizure characteristics (hypersalivation, jaw-clenching, involuntary swallowing .etc) pose some difficultes with regard to oral administration.[25][26]
Lorazepam’s anticonvulsant and CNS depressant properties are useful for the treatment and prevention of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. In this setting, impaired liver function is not a hazard with lorazepam, since lorazepam does not require oxidation, in the liver or otherwise, for its metabolism. Lorazepam is noted as being the most tolerable benzodiazepine in those with advanced-stage liver disease.[27][28][29]
Sedation
Lorazepam is sometimes used for individuals receiving mechanical ventilation. However, in critically ill people, propofol has been found to be superior to lorazepam both in effectiveness and overall cost; as a result, the use of propofol for this indication is now encouraged, whereas the use of lorazepam is discouraged.[30]
Its relative effectiveness in preventing new memory formation,[31] along with its ability to reduce agitation and anxiety, makes lorazepam useful as premedication. It is given before a general anesthetic to reduce the amount of anesthetic required, or before unpleasant awake procedures, such as in dentistry or endoscopies, to reduce anxiety, to increase compliance, and to induce amnesia for the procedure. Lorazepam by mouth is given 90 to 120 minutes before procedures, and intravenous lorazepam as late as 10 minutes before procedures.[32][33][34] Lorazepam is sometimes used as an alternative to midazolam in palliative sedation.[35] In intensive care units lorazepam is sometimes used to produce anxiolysis, hypnosis, and amnesia.[36]
Agitation
Lorazepam is sometimes used as an alternative to haloperidol when there is the need for rapid sedation of violent or agitated individuals,[37][38] but haloperidol plus promethazine is preferred due to better effectiveness and due to lorazepam’s adverse effects on respiratory function.[39] However, adverse effects such as behavioral disinhibition may make benzodiazepines inappropriate for some people who are acutely psychotic .[40] Acute delirium is sometimes treated with lorazepam, but as it can cause paradoxical effects, it is preferably given together with haloperidol.[41] Lorazepam is absorbed relatively slowly if given intramuscularly, a common route in restraint situations.
Other
Catatonia with inability to speak is responsive to lorazepam. Symptoms may recur and treatment for some days may be necessary. Catatonia due to abrupt or overly rapid withdrawal from benzodiazepines, as part of the benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, should also respond to lorazepam treatment.[42] As lorazepam can have paradoxical effects, haloperidol is sometimes given at the same time.[41][43]
It is sometimes used in chemotherapy in addition to medications used to treat nausea and vomiting, i.e. nausea and vomiting caused or worsened by psychological sensitization to the thought of being sick.[44]
| Quantity | 90 Pills, 180 Pills |
|---|
Be the first to review “Ativan Lorazepam 2.5mg” Cancel reply
Related products
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS
PHARMACEUTICALS








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.